Affordable and Accurate Diabetes Watch: Revolutionizing Your Health Monitoring
In an effort to enhance diabetes management, many individuals are opting for an budget friendly diabetes watch. These devices simplify self-monitoring and help reduce long-term complications. By using sensors to meticulously monitor glucose levels through the skin, these watches eliminate the need for constant finger pricking. Often FDA approved, they provide accurate and reliable readings, seamlessly integrating with diabetes management apps.
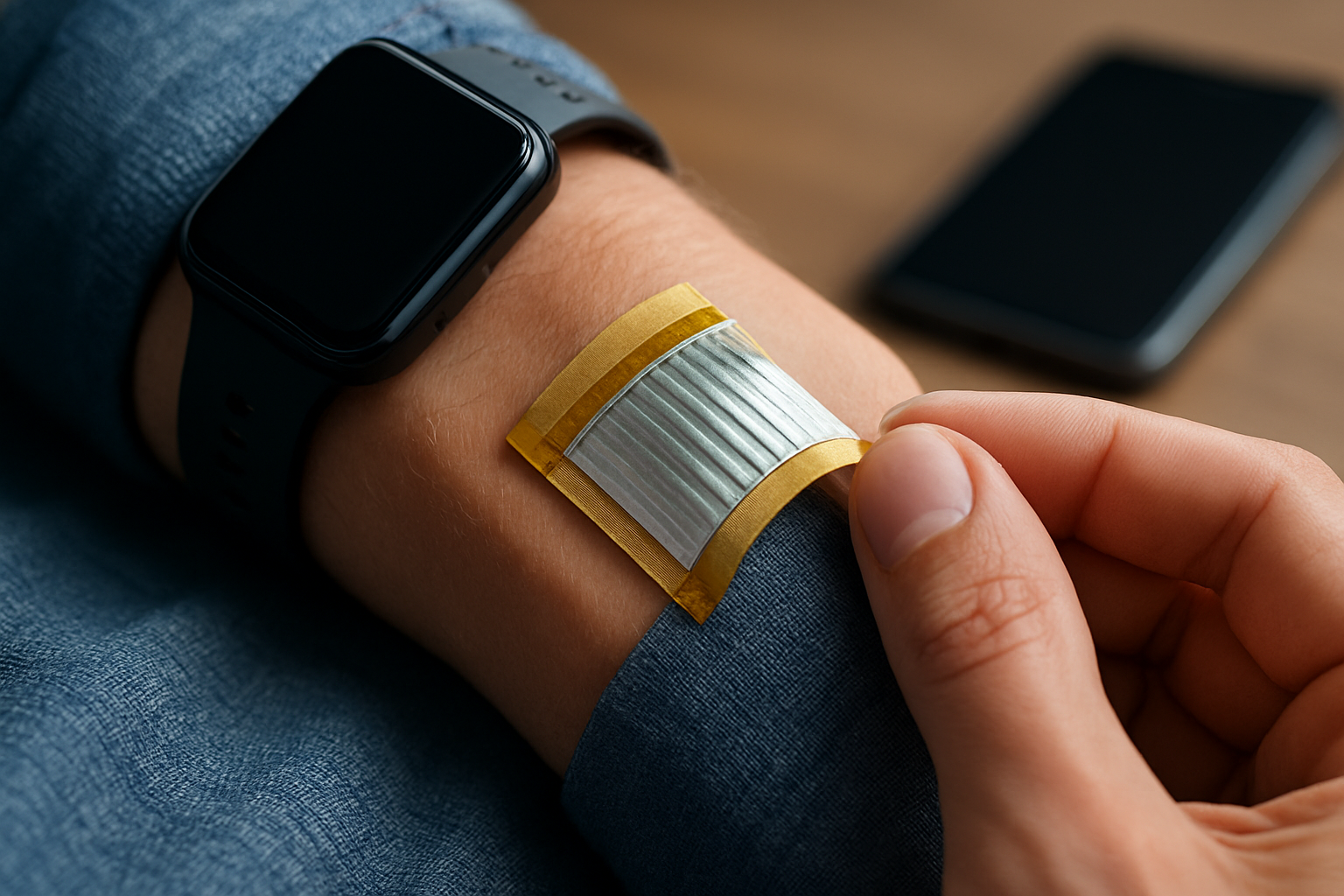

Diabetes management requires constant vigilance, and traditional blood glucose testing methods can be inconvenient and uncomfortable. Modern wearable technology has introduced a new era of diabetes care, where continuous monitoring happens seamlessly in the background while you go about your daily activities. These devices provide valuable data that helps users and healthcare providers make better treatment decisions.
What Is a Continuous Glucose Monitor?
A continuous glucose monitor is a small wearable device that tracks glucose levels throughout the day and night. Unlike traditional glucose meters that require finger pricks multiple times daily, these systems use a tiny sensor inserted just under the skin to measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid. The sensor wirelessly transmits data to a receiver, smartphone app, or compatible smartwatch, providing real-time readings every few minutes. This constant stream of information reveals patterns and trends that single point-in-time measurements might miss, giving users a comprehensive picture of how their body responds to food, exercise, medication, and stress.
How Does Glucose Management Improve With Wearable Technology?
Effective glucose management relies on understanding how your blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day. Wearable diabetes technology empowers users by providing immediate feedback on their glucose levels, allowing for quick adjustments to diet, activity, or medication. Many devices include customizable alerts that warn users when glucose levels are trending too high or too low, preventing dangerous situations before they occur. The historical data collected by these systems helps identify patterns, such as post-meal spikes or overnight drops, enabling more precise insulin dosing and lifestyle modifications. Healthcare providers can also review this data during appointments, leading to more personalized treatment plans based on actual patient behavior rather than estimates or recall.
What Are the Key Features of Modern Diabetes Monitoring Systems?
Today’s diabetes monitoring systems offer features that extend far beyond simple glucose readings. Most devices sync with smartphone apps that display trends, generate reports, and even predict future glucose levels based on current trajectories. Integration with smartwatches allows users to check their levels with a quick glance at their wrist, without pulling out a phone or separate device. Many systems calculate time-in-range metrics, showing what percentage of the day glucose levels stayed within target zones. Some advanced models can share data with family members or caregivers in real-time, providing peace of mind for parents of children with diabetes or adult children caring for elderly parents. Calibration requirements vary by device, with newer models requiring little to no finger-stick calibration.
How Accurate Are Blood Sugar Trackers Compared to Traditional Methods?
Accuracy is paramount when it comes to diabetes monitoring, as treatment decisions depend on reliable data. Modern continuous glucose monitors have achieved impressive accuracy rates, with many systems showing mean absolute relative differences of 9-10% compared to laboratory reference standards. While traditional finger-stick meters remain the gold standard for single-point accuracy, continuous monitors excel at revealing trends and patterns. The slight delay between blood glucose and interstitial glucose measurements means these devices may lag behind rapid changes by 5-10 minutes, which is why users are typically advised to confirm readings with a finger stick before taking corrective action for extreme highs or lows. Despite this limitation, studies consistently show that users of continuous monitoring systems achieve better overall glucose control and experience fewer dangerous episodes.
What Should You Consider When Choosing a Diabetes Care Device?
Selecting the right diabetes care device involves weighing multiple factors including accuracy, ease of use, cost, insurance coverage, and lifestyle compatibility. Sensor wear time varies from 7 to 14 days depending on the model, affecting how often you need to change sensors. Some systems require a separate receiver while others work directly with smartphones or smartwatches. Water resistance ratings differ, which matters if you swim or shower frequently. Consider whether you want a device that integrates with insulin pumps for automated insulin delivery, a feature increasingly available in newer systems. Reading reviews from actual users can provide insights into real-world performance, comfort, and customer support quality that specifications alone cannot convey.
Real-World Cost Considerations and Device Comparisons
Understanding the financial aspects of continuous glucose monitoring helps you plan for this investment in your health. Costs vary significantly based on the system chosen, insurance coverage, and whether you purchase supplies through insurance or pay out-of-pocket.
| Device/System | Manufacturer | Approximate Monthly Cost | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dexcom G6 | Dexcom | $300-$400 without insurance | No calibration required, 10-day sensors, smartphone integration |
| FreeStyle Libre 2 | Abbott | $150-$200 without insurance | 14-day sensors, optional alarms, scanning required |
| Medtronic Guardian Connect | Medtronic | $350-$450 without insurance | Predictive alerts, calibration required, 7-day sensors |
| Eversense | Senseonics | $200-$300 monthly without insurance | Implantable 90-day sensor, vibration alerts |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Many insurance plans, including Medicare, now cover continuous glucose monitoring for qualifying patients. Out-of-pocket costs typically include initial receiver or transmitter purchases ranging from $200-$500, plus ongoing sensor costs. Some manufacturers offer patient assistance programs or subscription models that reduce upfront expenses. Pharmacy benefits may differ from durable medical equipment coverage, so checking both pathways with your insurance provider can sometimes reveal more affordable options.
How Can You Maximize the Benefits of Your Monitoring System?
Owning a diabetes monitoring device is just the first step; using it effectively requires engagement and understanding. Take time to learn your device’s features, including how to set appropriate alert thresholds that warn you without causing alarm fatigue. Review your glucose data regularly, looking for patterns related to meals, exercise, sleep, and stress. Share your data with your healthcare team and come to appointments prepared to discuss what you’ve learned. Many users find that keeping notes about activities, meals, and how they felt during certain glucose patterns helps identify triggers and solutions. Consider joining online communities or support groups where users share tips and experiences with similar devices. Remember that these tools provide information to guide decisions, but they work best when combined with proper medication adherence, healthy eating, regular physical activity, and ongoing medical care.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.